While Windows 8 apps work in sandbox with limited access to file system, WinRT provides two methods for accessing and manipulating files and folders on external storage devices, such us USB keys and external hard drives.
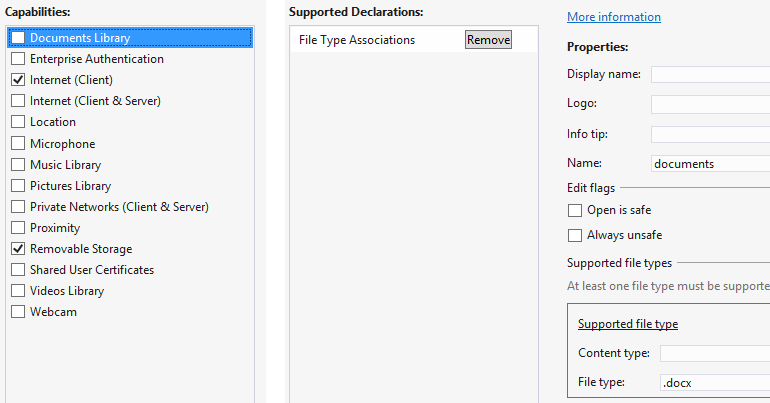
No matter which method is used, application’s manifest has to request Removable Storage capability and declare what file types will be used.
KnownFolders.RemovableDevices
By using Windows.Storage.KnownFolders.RemovableDevices application can get StorageFolder object that maps all removable devices as subfolders. For example, if there are three external hard drives plugged into computer, KnownFolders.RemovableDevices will contain three subfolders representing these drives.
var folders = await Windows.Storage.KnownFolders.RemovableDevices.GetFoldersAsync();
foreach (var storageFolder in folders)
{
var files = await storageFolder.GetFilesAsync();
// work with files
}
Notes:
- Returned files are filtered to file types declared in app manifest.
KnownFolders.RemovableDevicesfolder can be queried usingCreateFolderQuery, but ContentsChanged event is not fired when any of the devices is plugged or unplugged.
KnownFolders.RemovableDevices allows accessing removable storages such us DVD disks, USB keys, memory cards, external hard drives, etc.
StorageDevice and DeviceInformation
Alternatively, external storage devices can be accessed using combination of StorageDevice and DeviceInformation classes.
// Get all removable devices
var selector = Windows.Devices.Portable.StorageDevice.GetDeviceSelector();
var devices = await Windows.Devices.Enumeration.DeviceInformation.FindAllAsync(selector);
foreach (Windows.Devices.Enumeration.DeviceInformation device in devices)
{
// Get device root folder
StorageFolder rootFolder = Windows.Devices.Portable.StorageDevice.FromId(device.Id);
// Get files
var files = await rootFolder.GetFilesAsync();
// work with files
}
StorageFolder object returned by StorageDevice.FromId() represents the selected device’s root folder. Similar to RemovableDevices folder, the returned files are filtered.
DeviceInformation class allows accessing portable storage devices such as USB keys, memory card readers, mobile phones, etc. Note that sometimes DeviceInformation.FindAllAsync() can return device that doesn’t support file operations (e.g. Windows Phone). Method StorageDevice.FromId() called for such device will throw exception.
DeviceWatcher
Method DeviceInformation.FindAllAsync() returns current list of the devices. If application is interested in continuous monitoring of the devices, it can use DeviceWatcher.
var watcher = DeviceInformation.CreateWatcher(DeviceClass.PortableStorageDevice);
watcher.Added += Watcher_Added;
watcher.Removed += Watcher_Removed;
watcher.EnumerationCompleted += Watcher_EnumerationCompleted;
watcher.Stopped += Watcher_Stopped;
watcher.Start();
DeviceWatcher supports four events:
- Added to track newly plugged devices. Also Added event is fired when watcher is started, for each already plugged device.
- EnumerationCompleted is fired once when all devices plugged before watcher start are enumerated using Added event.
- Removed to track unplugged devices
- Stopped indicates end of watcher’s work
Watcher can be stopped using Stop() method.